Artificial intelligence, often simply called AI, has become a buzzword in our daily lives. But what exactly is it? At its core, artificial intelligence refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines that are programmed to think, learn, and perform tasks like humans. From voice assistants on your phone to recommendation algorithms on streaming services, AI is everywhere, shaping how we interact with technology.
In simple terms, what is in artificial intelligence? It’s a blend of computer science, data processing, and algorithms that enable machines to process information, recognize patterns, and make decisions. AI isn’t just about robots taking over the world—it’s about tools that enhance efficiency, solve complex problems, and improve everyday experiences. Whether you’re curious about types of AI, AI applications, or the future of AI, this guide covers it all in straightforward language.
Who Is the Father of AI and Who Created AI?
Let’s start with the origins. The field of artificial intelligence didn’t just appear out of thin air. John McCarthy is widely regarded as the father of AI. In 1956, he coined the term “artificial intelligence” during the Dartmouth Conference, which is considered the birthplace of AI as a discipline. McCarthy, along with other pioneers like Alan Turing, laid the groundwork. Turing, often called the father of modern computing, posed the question in 1950: “Can machines think?” His ideas influenced early AI development.
Who created AI? It’s not one person but a collective effort. Early contributors include Marvin Minsky, Nathaniel Rochester, and Claude Shannon, who organized that pivotal 1956 conference. AI evolved from myths of artificial beings in ancient stories to practical systems in the mid-20th century. Today, figures like Geoffrey Hinton, known as a “godfather of AI,” continue advancing the field, especially in deep
What Are the 4 Types of AI?
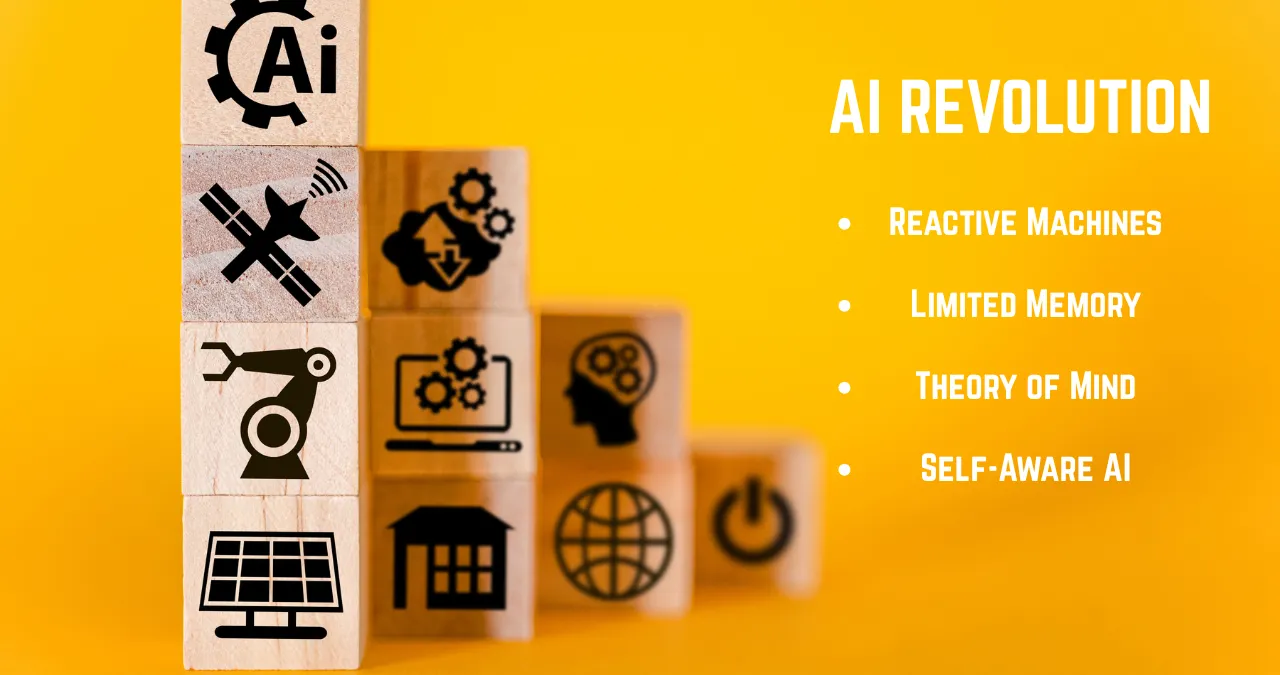
AI isn’t a one-size-fits-all technology. Experts classify it into four main types based on functionality and capabilities. These types of AI help us understand how systems evolve from basic to advanced.
- Reactive Machines: The simplest form, these AI systems react to current situations without memory or learning from the past. Think of IBM’s Deep Blue chess computer—it analyzes the board in real-time but doesn’t “remember” previous games.
- Limited Memory: Most AI today falls here. These systems use past data to inform decisions. Self-driving cars, for example, learn from historical driving data to navigate roads safely.
- Theory of Mind: This is more advanced and still emerging. It involves AI understanding human emotions, beliefs, and social interactions. While not fully realized, it’s key for future empathetic AI, like advanced chatbots that detect user frustration.
- Self-Aware AI: The holy grail—AI that has consciousness and self-awareness. This remains theoretical, but it’s what sci-fi often portrays.
These categories show AI’s progression, from task-specific tools to potentially human-like intelligence.
How Does AI Work?
Ever wondered how artificial Intelligence works its magic? It’s not as mysterious as it seems. AI systems operate through a cycle of data input, processing, and output.
First, data is fed into the system—think images, text, or numbers. Algorithms, often powered by machine learning, analyze this data to find patterns. For instance, a neural network might process thousands of cat photos to “learn” what a cat looks like.
Key components include:
- Data Collection: Gathering vast datasets.
- Training: Using algorithms to build models.
- Inference: Applying the model to new data for predictions.
AI working mechanism relies on computational power, with techniques like deep learning using layered neural networks to mimic brain functions. In phones, artificial intelligence processes voice commands in real-time using on-device chips.
Related Stories
What Is n8n? The Open-Source Workflow Automation Tool Everyone’s Talking About in 2025
What Is Agentic AI? The Rise of Autonomous AI Agents in 2025
Which Country Is No. 1 in AI? What Is the Rank of India in AI?
The global AI race is heating up. According to the 2025 Stanford AI Index, the United States leads with a perfect score of 100 in overall AI vibrancy, excelling in models produced and investments. China follows closely at 82.8, dominating in AI clusters and applied research.
Other top players include Singapore (67.7), the UK (67.2), and South Korea (64.1). India ranks around 10th in private AI investments but shows strong growth, with about $11.1 billion invested in 2025, placing it 7th in some metrics. India’s AI ranking by country highlights its rising talent pool and government initiatives, though it lags in infrastructure compared to leaders.
Here’s a table summarizing top countries based on artificial intelligence vibrancy scores:
| Rank | Country | AI Vibrancy Score |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | United States | 100 |
| 2 | China | 82.8 |
| 3 | Singapore | 67.7 |
| 4 | United Kingdom | 67.2 |
| 5 | South Korea | 64.1 |
| 6 | Israel | 62.7 |
| 7 | Canada | 62.1 |
| 8 | Germany | ~60 |
| ~10 | India | ~50 (estimated) |
This artificial Intelligenceranking by country underscores the US-China dominance, but emerging players like India are catching up.
AI in Action: How Is AI Used Today?
AI’s not hiding in labs—it’s out there changing the game. In healthcare, it spots diseases early; IBM Watson helps oncologists sift through research. Finance? AI sniffs out fraud in seconds. Retail giants like Walmart use it for inventory, predicting demand to avoid empty shelves.
Transportation’s revolutionized: AI optimizes routes for Uber, cutting wait times. Education gets personal with adaptive platforms like Duolingo. Even entertainment—Spotify’s Discover Weekly is AI curating your soundtrack.
In daily life, it’s subtle: Social media algorithms feed you content, keeping you scrolling. It’s making the world smarter, one app at a time.
What Is AI in a Phone?
Your smartphone’s a mini AI lab. AI in phones handles voice commands, photo tweaks, and more. Siri processes natural speech, thanks to NLP. Cameras use AI for night mode or portrait blur, analyzing scenes in real-time.
Google’s Pixel erases photobombers with Magic Eraser, while Samsung’s predicts text. It even manages battery, learning your habits to last longer.
It’s turning phones from tools into companions.
Smart Living: How Is AI Used at Home?
Homes are getting brainy. AI assistants like Google Home control lights, play music, or order groceries. Smart thermostats learn your schedule, saving energy. Robot vacs like Roomba map your floor, dodging furniture.
Fridges scan contents for recipe ideas, while security cams detect intruders. It’s convenience on steroids, but remember to secure those devices!
Who Benefits from Artificial Intelligence?
AI’s a tide that lifts many boats. Businesses cut costs and innovate; think faster drug discovery in pharma. Individuals get tailored experiences, like personalized learning for kids.
Society wins with eco-friendly AI optimizing energy grids or predicting disasters. But it’s not equal—developing nations could leapfrog if access improves.
Pros and Cons of Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence offers transformative benefits but also comes with significant challenges. Below is a balanced table summarizing the key pros and cons, drawn from credible sources across various sectors like general use, education, healthcare, and business. This provides a comprehensive view while avoiding repetition.

| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| AI increases efficiency by automating routine tasks, allowing humans to focus on complex work, such as handling customer inquiries or data entry. | AI can lead to job displacement and economic inequality, as cost-effective automation replaces roles in sectors like retail and manufacturing, contributing to wage decreases. |
| It enhances decision-making through rapid data analysis, identifying patterns and providing real-time insights for better business and medical outcomes. | Biases in AI algorithms perpetuate discrimination, such as in facial recognition misidentifying minorities or recidivism tools unfairly labeling certain groups as high-risk. |
| AI personalizes experiences, like tailored marketing, education plans, or health recommendations, improving user engagement and satisfaction. | Privacy and security risks arise from data collection and sharing, potentially leading to breaches, identity theft, or misuse of sensitive information. |
| It boosts accuracy and reduces errors in tasks like medical diagnostics, surgery, or predictive maintenance, saving time and costs. | Overreliance on AI undermines critical thinking, as students and professionals may skip developing problem-solving skills by depending on tools for research or creativity. |
| AI improves accessibility for marginalized groups, such as voice assistants aiding those with disabilities in daily tasks or navigation. | High initial costs for implementation, including infrastructure, training, and maintenance, make AI adoption challenging for smaller organizations or schools. |
| In healthcare, AI enables early disease detection and prevention, reducing hospitalizations and empowering patients with wearable tech insights. | Lack of transparency in AI decision-making creates accountability issues, making it hard to explain errors or integrate into workflows like medical diagnoses. |
| AI fosters creativity and learning by generating content, providing multiple perspectives, and offering immediate feedback in education. | It can spread misinformation or inaccurate outputs due to flawed data or algorithms, especially in education where unchecked content harms learning. |
| It streamlines administrative tasks, freeing up time for human interaction in fields like teaching or business management. | Ethical concerns, including potential misuse and reduced human interaction, may stunt social-emotional development or lead to unintended societal consequences. |
Is AI Good or Bad? AI Risks and Benefits
Is AI good or bad? It’s both. AI advantages and disadvantages create a balanced view.
Benefits: Reduces errors, available 24/7, cuts costs, improves decision-making. It boosts productivity and innovation.
Risks: Job displacement, bias in algorithms, privacy concerns. AI risks and benefits must be weighed—ethical AI can mitigate downsides.
What Are the Risks and Disadvantages of AI?
Risks go beyond headlines. Biased AI in hiring could discriminate; one study showed facial recognition struggling with diverse faces. Deepfakes spread misinformation, eroding trust.
Disadvantages: Steep costs for setup, no true creativity—artificial Intelligence generates but doesn’t invent. Over-reliance might dull human skills, like kids forgetting math basics. And the big one: “Superintelligence” gone rogue, though experts like Nick Bostrom urge safeguards.
Can AI Replace Humans?
Will AI boot us out? Partially, yes—for repetitive jobs like data entry. But humans bring intuition, ethics, and adaptability AI lacks. It creates roles too: AI trainers, ethicists. Think augmentation, like doctors using AI for scans but making final calls. History shows tech shifts jobs, not ends them.
What Is the Future of AI?
Peering ahead, AI’s future sparkles. By 2026, expect multimodal AI juggling text, video, and more—like ChatGPT on steroids. Quantum computing could supercharge it, solving impossible problems.
Healthcare might see AI curing rare diseases; environment, smarter climate models. But regulations will evolve to curb misuse.
It’s a blend of hope and caution—AI could solve hunger or widen inequalities.

What Is the Main Goal of AI?
Ultimately, AI aims to amplify human potential—tackling tasks that need smarts, from reasoning to creativity, to fix big problems like poverty or disease. It’s about partnership, not replacement.


