This guide will teach you how to make an automated WordPress website that runs itself. It doesn’t matter if you’re new to web development or an experienced site owner looking for ways to make things easier. You will learn how to make things like publishing content, making backups, and marketing easier. This will save you hours and help your business grow and become more reliable.
Why Automate Your WordPress Site in 2025?
In 2025, you’ll need to automate your WordPress site to stay competitive in a fast-paced digital world. WordPress is used by about 43.4% of all websites in the world, so it’s important to take care of it well. An automated WordPress website does things that need to be done over and over again without anyone’s help. This lets you focus on strategy and being creative.
The main benefits are that they save time. Posting to social media, updating plugins, and sending email newsletters by hand can take up to 20 hours a week. Automation tools make these tasks happen without any problems. For example, when you publish a new blog post, it could automatically share it on X , add it to your email list, and log it in Google Sheets. This not only cuts down on mistakes, but it also makes sure that tasks are done on time, no matter what.
Another big benefit is that you can scale content distribution. Automation helps you reach more people at a time when content marketing brings in 67% more leads than other methods. Tools can share posts on different platforms, improve them for search engines, and even A/B test headlines. This helps small teams compete with bigger ones. For e-commerce sites, automation can start marketing tasks like sending emails to people who left items in their cart or making personalized recommendations. This could boost conversions by as much as 30%.

Cutting down on manual work also lowers risks. Automated backups and security scans keep your data safe, and update schedulers keep your site safe from security holes. This is very important because WordPress sites are attacked every 32 minutes on average. Companies that use workflow automation say their productivity goes up by 25–30%, their errors go down by 40–75%, and their employees are happier by 15–35%.
Why should you automate WordPress now? The platform’s ecosystem has matured, and AI integrations and tools that don’t require coding make it easier to use. Automation keeps low-traffic sites reliable, even when traditional scheduling might not work, as more people work from home. According to market predictions, the market for workflow automation will grow from $5 billion in 2018 to $26 billion in 2025. This shows how important it is. This means that site owners can make money without doing anything by using streamlined affiliate marketing or membership sites. In the end, an automated WordPress website turns your site from a static asset into a dynamic machine that makes money.
Core Concepts: How WordPress Automation Works
Understanding the fundamentals of WordPress automation is crucial before diving into implementation. At its heart, automation leverages scheduled tasks, triggers, and actions to handle processes efficiently, reducing the need for constant oversight.
WP-Cron vs Server Cron: What Actually Runs Scheduled Tasks
WordPress uses WP-Cron, a pseudo-cron system, to manage scheduled events like publishing posts, checking for updates, or running backups. Unlike a true UNIX cron job that runs at precise intervals on the server, WP-Cron is triggered by page loads. When a visitor accesses your site, WordPress checks for due tasks and executes them. This works well for high-traffic sites but falters on low-traffic ones, where delays can occur if no loads happen at the scheduled time—potentially postponing critical actions like email sends or plugin checks.
For reliability, especially in 2025 with increasing reliance on real-time operations, switch to a real server cron. This runs independently of traffic, ensuring tasks execute on time. Managed hosts like WordPress VIP enhance WP-Cron for enterprise use by using optimized tables and parallel processing, but for standard sites, disable WP-Cron in wp-config.php by adding define(‘DISABLE_WP_CRON’, true); and set up a server cron job. A common setup calls wp-cron.php every 5-15 minutes via a command like */5 * * * * wget -q -O – https://your-site.com/wp-cron.php?doing_wp_cron >/dev/null 2>&1 or using curl for better performance. This prevents overload and improves uptime, as VIP’s system processes up to 60 jobs per hour in parallel.
Triggers & Actions Model (No-Code Automators)
The triggers and actions framework makes no-code automation possible, which makes it easier to use complex workflows. A trigger is an event that starts the process, like a new post being published, a form being submitted, or a user logging in. Then you can tweet the post, add data to a CRM, or send an email.
Uncanny Automator is an example of a plugin that does this: It links more than 210 apps and has more than 8,700 variables for dynamic recipes. It also supports delays, conditions, and webhooks. For instance, a trigger like “post published” could cause sharing to X, sending a message to Slack, and updating Sheets—all without any code. AutomatorWP is an open-source alternative that has more than 600 triggers and actions across more than 200 plugins. It also has filters for conditional logic and sequential execution.
This model can grow: it works with AI on business sites to personalize content or with e-commerce to fill orders. There are many benefits, such as unlimited runs (Uncanny says it has 110 million successful recipes) and data privacy because processing stays on-site. Hooks let advanced users add their own functions, which combines the ease of no-code with the freedom of a developer.
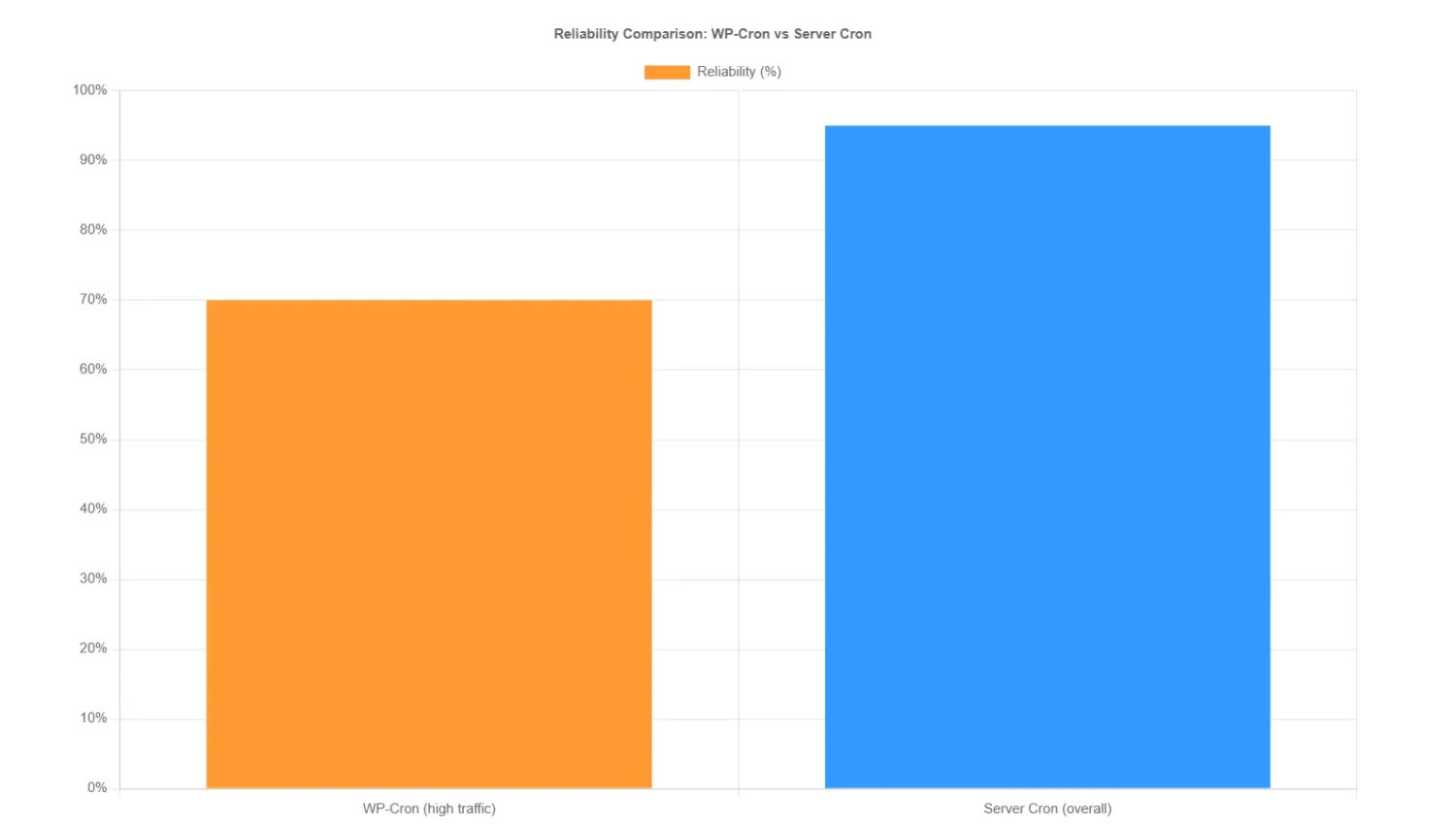
Reliability Comparison Table
| Reliability Factor | WP-Cron | Server Cron |
|---|---|---|
| Low Traffic | Low | High |
| Execution Timing | Delayed | Precise |
| Resource Use | Higher | Lower |
Plan Your Automation Roadmap
Before you put automation into place, check your site’s processes to see where they can be automated. Make a list of things you need to do, such as publishing content, sharing on social media, getting people to sign up for your email list, making backups, updating your site, scanning for security issues, and moderating comments. Check each one for how often it happens, how hard it is, and how much it costs—does it save you time or make you money?
Use a 3-item matrix to set priorities: First, safety (backups and updates to avoid downtime), then revenue (email sequences and product delivery for direct income), and finally marketing and operations (social sharing and reports for growth). Keep an eye on uptime (aim for 99.9%), email conversions (aim for 20–30% open rates), and time saved (use tools like Toggl to measure hours before and after automation).
This roadmap makes sure that growth can be scaled: Start with the most important safety nets and then add revenue drivers on top of them. In 2025, when 80% of businesses are using more automation, a planned approach keeps things from getting too busy and gets the most return on investment.
Tech Stack & Plugin Recommendations (Actionable)
Building an automated WordPress site requires the right tools. Here’s a curated list of proven plugins and platforms, with pros/cons and use cases.
Automation Plugins (In-WordPress):
- Uncanny Automator: No-code recipes connecting 210+ apps like WooCommerce and Google Sheets. Pros: Unlimited usage, 8,700+ tokens for dynamics, conditions/delays; Cons: Pro version needed for advanced features ($149/year). Use case: Automate course enrollments in LearnDash upon form submission.
- AutomatorWP: Open-source with 600+ triggers/actions for WP plugins. Pros: Free core, sequential logic, filters; Cons: Premium add-ons for webhooks ($99/year). Use case: Reward users with badges after multiple comments via BuddyPress integration.
External Automation / Integration Platforms:
- Zapier: Links WordPress to 5,000+ apps like Slack and CRMs. Pros: Easy zaps (e.g., new post to LinkedIn), free tier; Cons: Paid for multi-step ($19.99/month). Use case: Sync form leads to Mailchimp and Google Sheets.
- n8n: Self-hosted for advanced workflows. Pros: Code/UI flexibility, no vendor lock-in, 500+ apps; Cons: Requires setup knowledge. Use case: Custom AI agents for content personalization via WordPress APIs.
Developer Ops:
- WP-CLI: Command-line for maintenance. Pros: Scriptable (e.g., wp plugin update –all); Cons: CLI access needed. Use case: Cron-controlled updates: wp cron event run –due-now.
For hosting, choose providers supporting real cron and WP-CLI (e.g., SiteGround, WP Engine). Check docs for restrictions—managed hosts may limit but offer built-in automation.
Step-by-Step Build & Implementation
Follow these six steps for a robust automated setup. I’ll keep commands and examples short and clear so you can paste them into your server or share with a developer.
Step 1 — Choose hosting and enable cron & WP-CLI
Pick a host that lets you run real cron jobs and gives SSH access so you can use WP-CLI. Managed hosts often let you run system cron and WP-CLI; if you’re unsure, ask support whether they allow crontab and wp (WP-CLI).
On low-traffic sites the built-in WP-Cron only runs when someone visits a page, so it can be delayed. To stop WordPress from trying to run cron on every page load, add this just above the /* That's all, stop editing! */ line in wp-config.php:
define('DISABLE_WP_CRON', true);
Then set a system cron job to hit your site on a schedule. Two common options:
- Call the wp-cron URL (easy, works everywhere):
*/5 * * * * curl -s https://example.com/wp-cron.php?doing_wp_cron >/dev/null 2>&1
- Or, if you have WP-CLI available (more reliable):
*/5 * * * * cd /path/to/wordpress && wp cron event run --due-now >/dev/null 2>&1
After that, you can inspect scheduled events with WP-CLI (wp cron event list) and run due jobs manually (wp cron event run --due-now) to test. Back up wp-config.php before editing and confirm cron runs under the correct user/path on your host.
Step 2 — Install core automation plugins and connect accounts
Install your automation plugin either from the dashboard (Plugins → Add New) or quickly with WP-CLI. For example, to install Uncanny Automator via WP-CLI:
wp plugin install uncanny-automator --activate
Once installed, go into the plugin’s settings and connect any external apps (Google, Slack, Twitter/X, etc.). Most plugins ask you to authorize via OAuth or paste an API key — follow their on-screen flow. If you plan to use Zapier or n8n instead, those also connect via webhooks or small connector plugins.
tep 3 — Create your first automation recipes (real examples)
Start small. Build and test one recipe at a time so you don’t accidentally spam users or publish bad content.
Example A — New post → Social + Sheet + Slack
- Trigger: New post published.
- Actions: Post a summary to X, add a new row to a Google Sheet with title + URL, and send a Slack message to your editorial channel.
How: In Uncanny Automator (or Zapier), pick “Post published” as the trigger, then add actions for Google Sheets, X, and Slack. Test with a draft post first.
Example B — Lead capture → CRM + Email sequence
- Trigger: Web form submitted.
- Actions: Create/update contact in your CRM, tag them, and add them to an automated welcome email sequence.
Example C — Weekly maintenance
- Trigger: System cron (weekly).
- Actions: Run
wp plugin update --all, create a backup, and email the admin a short report. You can implement this with a shell script + WP-CLI or a scheduled automation recipe.
Always create a test/staging recipe first and verify each action completes correctly before moving to production.
Step 4 — Safety checks & human review
Automation is powerful — but mistakes scale too. Put human gates where it matters:
- For public content: have automation create drafts or “pending review” instead of publishing immediately. That gives editors a chance to check facts, tone, links, and E-E-A-T (expertise / experience / authoritativeness / trust).
- For payments or access: require a confirmation step or manual check before granting purchases/memberships.
- For AI-generated copy: always add an editor review and a short disclosure (e.g., “This draft was AI-assisted and edited by our team”).
These small checks prevent embarrassing errors and protect your site reputation.
Step 5 — Monitoring, logging & rollback
Make sure you can see what your automations do and react if something goes wrong.
- Keep logs: Use the plugin’s built-in logs (most automation plugins show recent runs and errors).
- Alerting: Send failure alerts to Slack/email so you notice ASAP. For example, if a post fails to publish three times, send a Slack message.
- Test on staging: Always run new recipes on a staging site first.
- Rollback plan: For risky automations (e.g., bulk updates), snapshot the database or use your backup plugin before running. If something breaks you can revert the backup or deactivate the automation quickly with WP-CLI or from the dashboard.
These practices mean problems are visible and recoverable.
Step 6 — Iterate and measure
Automation is not “set and forget.” Track how it performs and refine.
- KPIs to watch: success rate (target 95%+), time saved per week, email signups from automated flows, social clicks from automated posts, number of failed runs.
- Improve slowly: if a recipe fails often, add throttles or retries (don’t hammer APIs). For high-volume tasks, add rate limits or batching.
- A/B test: try slightly different automation flows (e.g., immediate publish vs. human review) and measure which drives better engagement.
Use logs + analytics (events in Google Analytics / GA4) to prove automation is helping, then expand the ones that work.
SEO, AEO & Google Discover Optimization Checklist
To rank and appear in Discover, focus on people-first content: Avoid automation for low-value scraps; cite sources, add bylines/dates. E-E-A-T: Show expertise via credentials, editorial processes. Discover: No clickbait, high-res images (1200px+), good UX. Optimize Core Web Vitals via Console. Use Article schema; alt text with keywords.
Security, Backups & Legal
When you automate WordPress, security should always be the first thing you think about. It’s a good idea to lock down automations because they can make new ways for people to get into your site. To stop bots from starting workflows, use CAPTCHA on forms, set rate limits so an endpoint can’t be flooded with requests, and always check requests with signed webhooks to make sure the data really comes from the source you trust.
Backups are your safety net. Before running any major automation, schedule backups so you can roll back quickly if something breaks. Most reliable hosts provide snapshot or scheduled backups, but you can also use plugins like UpdraftPlus to store copies in Google Drive, Dropbox, or Amazon S3. Automations can fail — having a fallback plan saves hours of recovery.
Lastly, don’t forget about the law. You must follow data protection laws like GDPR in the EU or CCPA in California if your automations handle user data. That means being honest about how you handle data, keeping it safe, and letting users control their own information. Your privacy policy should list all of your automations so that visitors know what’s going on behind the scenes.
FAQs About Automated WordPress Website
What is an automated WordPress website?
It’s a site where tasks like publishing, backups, or updates run automatically using plugins or workflows.
Is WP-Cron reliable for automation?
Not really on low-traffic sites; server-level cron jobs are far more stable.
Which plugins let me create no-code automations?
Tools like Uncanny Automator, AutomatorWP, and Zapier make automation possible without coding.
Best host for automation?
Choose a host with native cron and WP-CLI support—SiteGround, Cloudways, or similar.
How to test and rollback automations?
Use a staging site, monitor logs, and keep WP-CLI commands handy for quick rollbacks.
Can automation publish AI-generated content?
Yes, but always add human editing to maintain quality, trust, and E-E-A-T compliance.
Does automation slow down WordPress?
Not if set up right—lightweight plugins, server cron, and caching ensure smooth performance.
Is automation safe for SEO?
Yes, as long as automations follow Google’s guidelines, use human oversight, and avoid spammy practices.
AI in automation?
AI can personalize content, recommend products, or trigger smart workflows when integrated with your setup.
Don’t Miss This: How to Start AI Autoblogging with WordPress (Step-by-Step Guide)
Don’t Miss This: How to Start an Automated YouTube Channel Using AI Tools